How to Identify and Observe Northern Cranes in Their Natural Habitat
Northern cranes are remarkable birds that captivate the minds of both birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts alike. With their striking appearance and graceful movements, these avian wonders are a sight to behold in their natural habitat. Understanding how to identify and observe northern cranes is essential for anyone looking to appreciate their beauty and conservation status. This guide aims to provide enthusiasts with clear and concise methods for spotting these majestic birds while respecting their living environments.
To successfully identify northern cranes, it is crucial to familiarize oneself with their physical characteristics and vocalizations. These birds often inhabit wetlands, open fields, and large agricultural landscapes, making certain regions ideal for observation. Furthermore, knowing the most active times of day for northern cranes can enhance your chances of witnessing their captivating behaviors, such as mating dances and foraging.
As we explore the various aspects of identifying and observing northern cranes, we will delve into the best practices for birdwatching that ensure minimal disturbance to their habitat. By learning to identify these magnificent creatures and their essential ecosystems, we can contribute to their conservation and enjoy the invaluable experience of witnessing them in the wild.
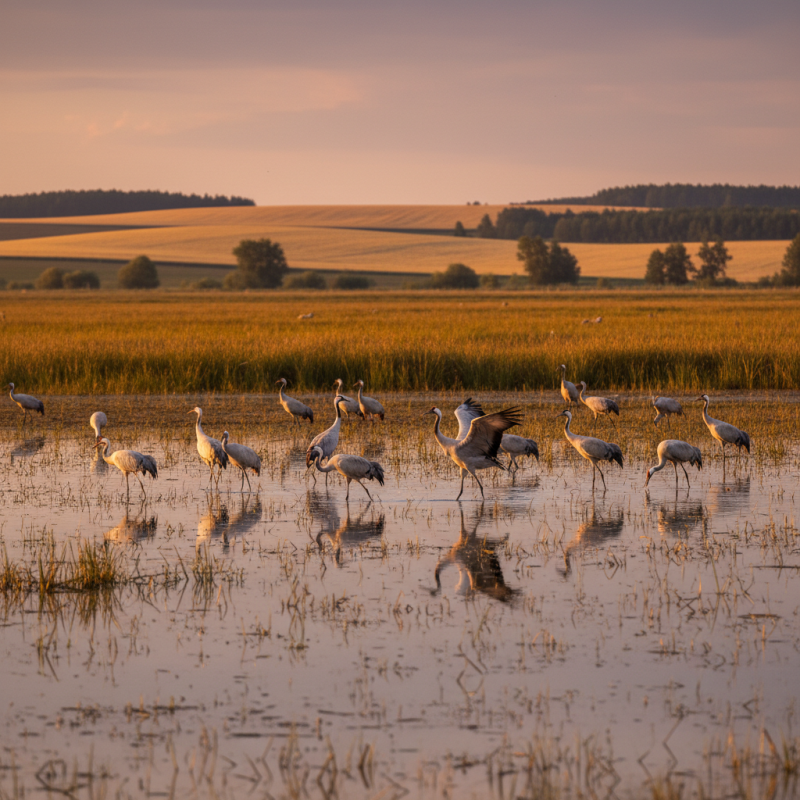

Identifying Key Characteristics of Northern Cranes in the Wild

Northern cranes are magnificent birds that capture the attention of nature enthusiasts and birdwatchers alike. To observe these graceful creatures in their natural habitat, it is crucial to identify their key characteristics. Generally, northern cranes can be distinguished by their impressive height, which often exceeds three feet, and their long legs that allow them to wade through marshes and wetlands with ease. Their plumage typically features a striking combination of gray and white, complemented by a distinctive red crown on their heads. Pay attention to their vocalizations as well, as each species has a unique call that resonates across their environment.
Tips: When identifying northern cranes, consider the time of year and location. They are often found in wetlands during migration seasons, so research local birdwatching hotspots ahead of time. Observing the cranes during dawn or dusk can also increase your chances of witnessing their elegant dancing displays, which are crucial for courtship and social interaction.
In addition to visual characteristics, understanding their behavior is key to successful observation. Northern cranes often form small family groups or larger flocks, especially during migration. Watching how they interact with each other can provide insights into their social structure and habits. Be patient and remain at a distance to avoid disturbing them; this will ensure a more rewarding and respectful observation experience.
Seasonal Migration Patterns of Northern Cranes and Their Habitat Use
Northern cranes, particularly the species like the Sandhill and Whooping cranes, exhibit fascinating seasonal migration patterns that are crucial to their survival. According to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, these birds travel thousands of miles between their breeding and wintering grounds, with the Sandhill cranes, for instance, traveling from as far north as Canada to southern states like New Mexico and Texas. This migration typically occurs in the spring and fall, aligning with favorable weather conditions and food availability during their journey.
The habitat use of northern cranes during migration is closely linked to agricultural landscapes and wetland areas. Research by the Crane Conservation Association indicates that these birds prefer open fields for foraging and shallow water bodies for resting. In particular, during their stopovers, cranes are often found in rice fields and wet meadows, where they can find ample food sources like grains and insects. Conservation efforts have highlighted the importance of protecting these critical habitats, as they are essential for the cranes to regain energy before continuing their long migrations. Maintaining the integrity of these environments not only supports the cranes but also promotes biodiversity within the ecosystem.
Essential Tools and Techniques for Observing Northern Cranes
When it comes to observing Northern Cranes in their natural habitat, having the right tools and techniques is paramount for wildlife enthusiasts and researchers alike. One of the primary tools is a good pair of binoculars, ideally with a magnification of 8x42 or 10x42, which strikes a balance between viewing distance and stability. According to the American Birding Association, a quality set of binoculars enhances the birdwatcher’s experience, allowing for clear sight of these magnificent creatures from a distance that doesn’t disturb them. A spotting scope can also be incredibly beneficial, especially in areas where cranes congregate, providing an even closer look at their behavior and interactions.
In addition to optical equipment, understanding the best times and locations for crane observation is crucial. Northern Cranes are migratory birds that often gather in large numbers during the migratory seasons—spring and fall. Utilizing resources such as the Audubon Society's migration maps can greatly assist in identifying peak viewing times. Moreover, techniques like maintaining a low profile and using natural cover when observing the cranes can lead to more successful and ethical viewing experiences. Observers should consider the use of camera traps to document their findings without impacting the birds directly; this method is supported by studies from the Cornell Lab of Ornithology, which show that technology can enhance our understanding of avian behavior while ensuring minimal disturbance to wildlife.
Preferred Feeding and Nesting Habitats of Northern Cranes
Northern cranes are majestic birds that thrive in specific environments tailored to their feeding and nesting needs. These creatures prefer expansive wetlands and grasslands, where they can easily access a variety of food sources. Marshes, shallow lakes, and open fields are prime locations for them to forage on grains, tubers, and insects. The availability of water and abundant vegetation not only supports their diet but also provides essential cover from predators.
During the nesting season, northern cranes seek out areas that offer both safety and proximity to food supplies. They typically build their nests in dense marsh vegetation, allowing them to stay concealed while raising their young. The ideal nesting sites are often near water sources, which facilitate easy access to food and hydration for the chicks. These habitats are crucial during the breeding cycle, as they ensure the survival of the next generation while also supporting the adult cranes' nutritional needs. Observing these birds in their natural environments can be a rewarding experience, highlighting the importance of preserving their preferred habitats.
Conservation Status and Threats Facing Northern Crane Populations
The northern crane populations, including species such as the Sandhill Crane and the Whooping Crane, face several significant threats that jeopardize their survival in natural habitats. According to the International Crane Foundation, habitat loss remains one of the most pressing challenges. Over 90% of wetland habitats have been drained or altered for agricultural use across North America, leading to a decrease in suitable nesting and feeding grounds. This has resulted in habitat fragmentation, making it increasingly difficult for cranes to find safe areas for breeding and rearing their young.
Additionally, climate change poses a substantial risk to northern crane populations. Rising temperatures and erratic weather patterns can affect migratory routes and alter the availability of food sources. A report from the National Audubon Society indicates that climate change projections could potentially shift suitable habitats for crane populations northward, which may not be feasible given the constraints of human development and land use. Moreover, increased human activity in critical habitats due to urbanization and industrial development further threatens these birds by exposing them to disturbances and potential collisions.
Conservation efforts are crucial to mitigating these threats. Initiatives that focus on habitat restoration, protection of migratory pathways, and awareness campaigns are increasingly vital. The North American Crane Working Group emphasizes creating and managing habitats that cater specifically to northern cranes’ needs to ensure their populations can thrive despite the challenges posed by climate change and habitat destruction.
Related Posts
-

What is a Truck Crane and How Does it Work
-

Maximizing Efficiency: How Grove Cranes Are Shaping the Future of Construction with 20% Increased Productivity
-

What is a Central Crane and How Does it Improve Construction Efficiency
-
2025 Top 10 Ton Overhead Crane Features and Benefits You Need to Know
-

Top 10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Best US Crane Services
-

Why Investing in Construction Cranes Boosts Project Efficiency and Reduces Costs
